
eye) and is found only in afferent fibers
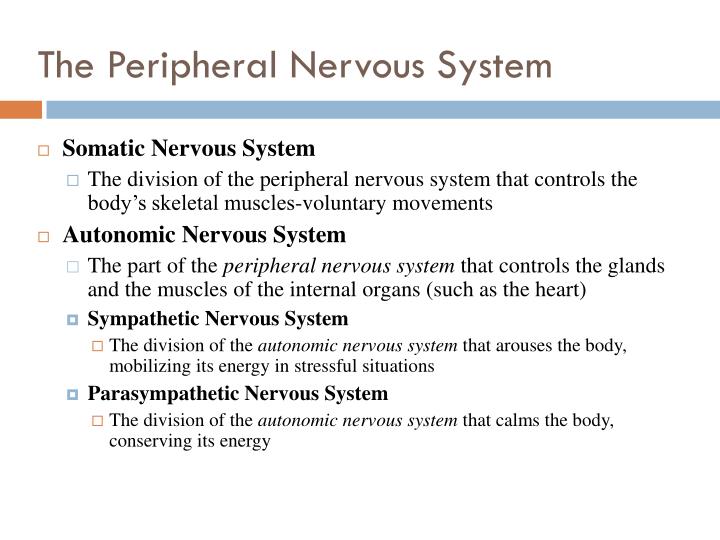
But you're in luck, as we've got a learning strategy for you to master neuroanatomy in a lot shorter time than you though you'll need. They say that the nervous system is one of the hardest anatomy topic. Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - described as the involuntary system.Somatic nervous system (SNS) - informally described as the voluntary system.Peripheral nervous system (PNS) - gathers all neural tissue outside the CNSįunctionally, the PNS is further subdivided into two functional divisions.Central nervous system (CNS) - consists of the brain and spinal cord.The nervous system (NS) is structurally broken down into two divisions These organs unite according to their common function, forming the evolutionary perfection that is our nervous system. So nervous tissue, comprised of neurons and neuroglia, forms our nervous organs (e.g. This significantly increases the speed of neural impulse propagation. The neural impulses propagate through the Ranvier nodes only, skipping the myelin sheath. Myelin encloses an axon segmentally, leaving unmyelinated gaps between the segments called the nodes of Ranvier. Most axons are wrapped by a white insulating substance called the myelin sheath, produced by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. The PNS doesn’t have a glial equivalent to microglia as the phagocytic role is performed by macrophages. Other two glial cell types are found in CNS exclusively microglia are the phagocytes of the CNS and ependymal cells which line the ventricular system of the CNS.Astrocytes(CNS) and satellite glial cells (PNS) both share the function of supporting and protecting neurons.Remember these easily with the mnemonic "COPS" ( Central - Oligodendrocytes Peripheral - Schwann) Myelinating glia produce the axon-insulating myelin sheath. These are called oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann cellsin the PNS.

This set of functions is provided for by four different types of glial cells Instead, they myelinate neurons, maintain homeostatic balance, provide structural support, protection and nutrition for neurons throughout the nervous system. Glial cells, also called neuroglia or simply glia, are smaller non-excitatory cells that act to support neurons. Understanding the nervous system requires knowledge of its various parts, so in this article you will learn about the nervous system breakdown and all its various divisions. Autonomic nervous system sympathetic, parasympathetic and enteric divisions It is further subdivided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS).Ī network of neurons that sends, receives and modulates neural impulses between different body parts. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) represents the conduit between the CNS and the body.Central nervous system (CNS) is the integration and command center of the body.The nervous system consists of two divisions Ultimately, the nervous system structures preside over everything that makes us human our consciousness, cognition, behaviour and memories. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements. The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
